AI’s Spotlight at CES and Intel’s Arrow Lake Announcement
The annual CES event has once again set the stage for groundbreaking technological advancements, with artificial intelligence (AI) stealing the limelight. Amidst the buzz, Intel has made a significant announcement that is poised to capture the attention of gaming enthusiasts and tech aficionados alike. The tech giant has unveiled plans to launch its next-generation CPU architecture for desktop PCs, codenamed Arrow Lake, slated for release in the latter half of 2024. This new offering is being heralded as the ‘world’s first gaming processor with an AI accelerator’, marking a milestone in the integration of AI capabilities directly into the gaming hardware realm.
Design and Manufacturing
Intel’s Arrow Lake represents an evolutionary step forward from its predecessor, the Meteor Lake design. It employs the innovative Foveros packaging system, which allows for the integration of multiple tiles—compute, graphics, SoC, IO—into a single stacked structure. This approach is somewhat akin to AMD’s chiplet design utilized in their Ryzen, Threadripper, and EPYC series. However, unlike AMD’s method where chips are physically separated within the CPU package, Foveros stacks these tiles onto a common substrate, minimizing the length of interconnects and potentially enhancing performance.
Arrow Lake also heralds a significant shift in semiconductor architecture, transitioning from the established FinFET (Field Effect Transistor) to the more advanced GaaFET (Gate-All-Around Field Effect Transistor), which Intel has branded as RibbonFET. This new architecture is expected to bring about improvements in performance and power efficiency.
Another innovation coming with Arrow Lake is PowerVia, Intel’s take on backside power delivery. This technology separates the input/output signaling connections from the power lines, applying power to the back of the wafer. This separation is anticipated to allow for higher clock speeds and a significant reduction in internal voltage drop.
| FinFET | GaaFET (RibbonFET) |
|---|---|
| 3D transistor design with current flowing on three sides | Advanced design with current flowing around a nanowire channel |
| Used for the past decade | Next-generation architecture |
| Less efficient at smaller scales | Improved efficiency and performance at smaller scales |
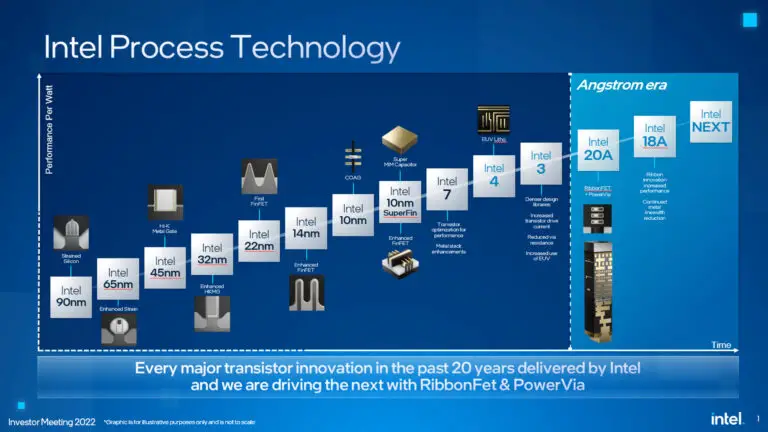
Process Node Evolution
The introduction of Intel’s 20A process node is a pivotal development in chip manufacturing, setting a new benchmark for the industry. This advanced process node is expected to significantly enhance the capabilities of semiconductor devices, offering a leap forward in terms of efficiency and performance.
Intel is not alone in its pursuit of innovation. Industry giants TMSC and Samsung are also on the path to adopting similar technologies, with plans to introduce their versions of GaaFET and backside power delivery systems. These advancements are anticipated to become more widespread in the industry either later this year or by 2025.
- Increased transistor density for more powerful and compact chips
- Enhanced power efficiency leading to lower energy consumption
- Improved performance with potential for higher clock speeds
- Reduced voltage drop for more stable power delivery
Performance Expectations
As we look towards the potential configurations of Intel’s Arrow Lake CPUs, we can speculate that they may offer an increase in core counts from the current Meteor Lake CPUs, which top out at six P-cores and eight E-cores. It’s plausible that Arrow Lake could launch with configurations featuring eight P-cores and 16 E-cores, with the possibility of even higher core counts as the architecture matures.
The graphics tile within Arrow Lake is also expected to see enhancements. While specifics remain under wraps, it’s reasonable to anticipate a larger graphics tile than that found in Meteor Lake, potentially boasting more shaders or even a newer architecture to further bolster gaming performance.
Central to the discussion of Arrow Lake’s capabilities is the inclusion of an NPU (neural processing unit) for AI acceleration. This feature is set to distinguish Intel’s offering from the competition, although it’s worth noting that AMD has already ventured into this territory with its Ryzen 7 8700G processor. The NPU within Arrow Lake is designed to handle machine learning operations efficiently, a feature that is becoming increasingly relevant in modern computing tasks.
Intel’s claim that Arrow Lake will be the ‘world’s first gaming processor with an AI accelerator’ may be a point of contention, considering AMD’s prior advancements. Nevertheless, the integration of AI acceleration into a gaming-focused CPU is a significant step forward for the industry.

The anticipation surrounding Intel’s Arrow Lake CPUs is palpable, especially considering the potential impact of the 20A process node on power efficiency and performance. The current 14th generation of desktop CPUs, while powerful, has drawn attention for its substantial power consumption. The promise of Arrow Lake, with its advanced process node, suggests a future where this power-hungry nature could be significantly mitigated.
As we look forward to the release of Arrow Lake, the prospect of a gaming chip that not only delivers raw performance but also operates more efficiently is an exciting development. If Intel can successfully leverage the 20A process node to resolve the power consumption issues of its predecessors, it may indeed have a ‘monster’ of a gaming chip on its hands. The integration of AI acceleration only adds to the allure, potentially setting a new standard for what gamers can expect from their hardware.
Ultimately, the true test will come when Arrow Lake hits the market and enthusiasts can evaluate whether the CPUs live up to the hype. Until then, the tech community waits with bated breath, eager to see how these advancements will shape the future of gaming and computing.